Big O notation tells how much solwer a piece of a program gets as the input gets larger. It describes the complexity of the code using algebraic terms.
The focus of Big O notation is on looking at the biggest trend of an algorithm, and the worst case how it scales as input size changes. Therefore, we only look at the slowest part of an algorithm.
Assuming the input size N is sufficiently large
- Ignore constants 상수항 무시
if O(n+5) -> O(n)
- Ignore coefficients 계수 무시
if O(3n) -> O(n)
- Only the highest-order term is noted 최고차항만 표기
if O(3n^3 + 2n^2 + n + 5) -> O(n^3)
Execution speed
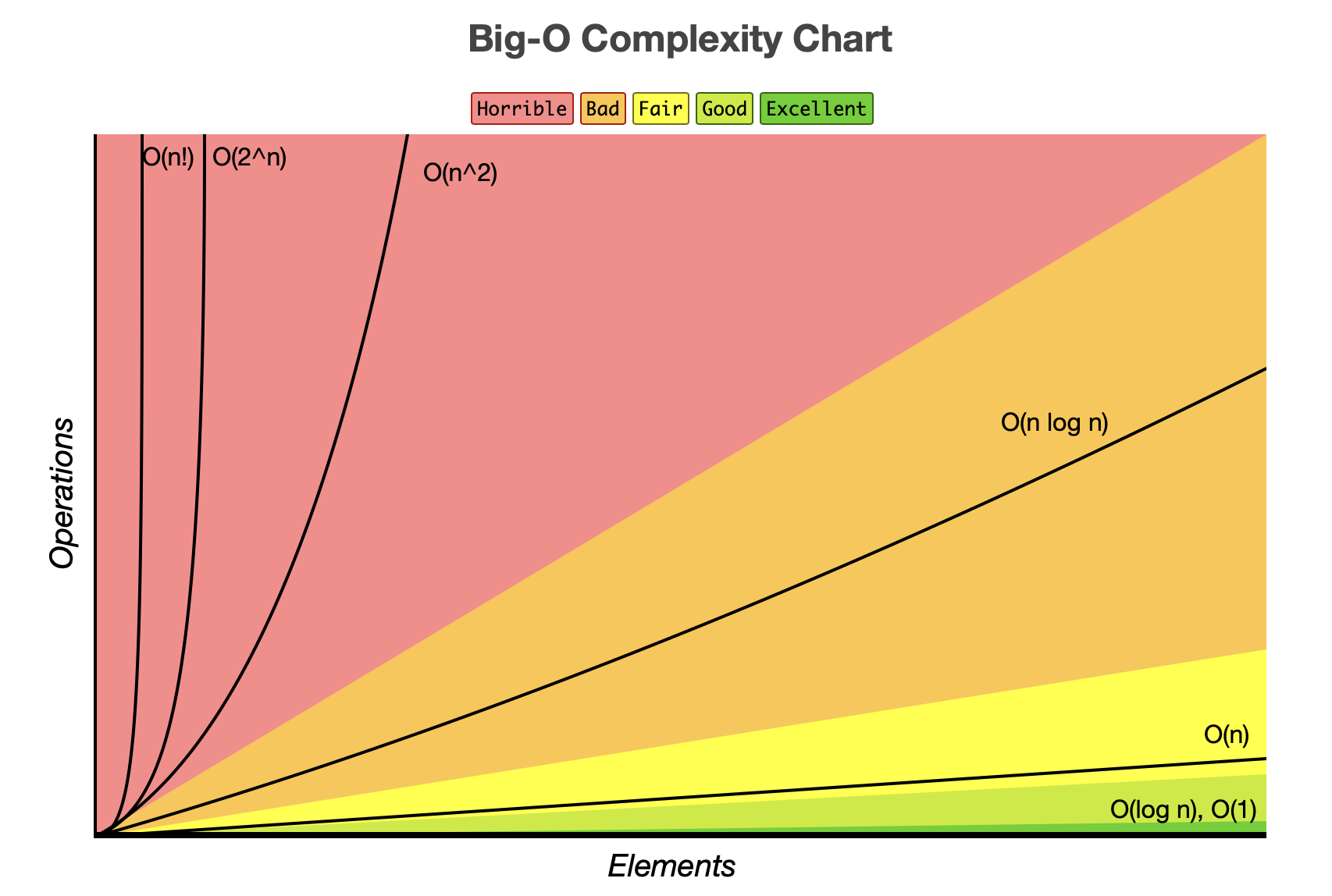
O(1) < O(log N) < O(N) < O(N log N) < O(N^2) < O(2^N)
Example
1. O(1)
when N increases, the execution time remains same.
ex) push, pop in simple stack
2. O(logN)
Algorithm that makes data became half after an execution.
ex) Binary search, Tree baed algorithm
3. O(N)
when N increases, the execution time increases linearly.
ex) for loop
4. O(NlogN)
An O(N) algorithm nested within an O(log N) algorithm.
ex) Quick sort, Merge sort, Heap sort
5. O(N^2)
An O(N) algorithm nested within an O(N) algorithm.
ex) nested for loop, insertion sort, bubble sort, selection sort
6. O(2^N)
Algorithm with the slowest time complexity often corresponds to those that are performed recursively.
ex) Fibonacci sequence, Recursive algorithms
Big-O Complexity Chart
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/big-o-notation-why-it-matters-and-why-it-doesnt-1674cfa8a23c/
https://www.reddit.com/r/computerscience/comments/s7h2vc/can_someone_explain_to_me_big_o_notation_like_im/
https://noahlogs.tistory.com/27
https://www.bigocheatsheet.com
