Feature Selection is the process of selecting a subset of relevant features for use in model construction.
It is different from feature extraction or dimensionality reduction.
It mostly acts as a filter, muting out features that aren’t useful in addition to your existing features.
The objective and importance of feature selection
- Improved Model Performance
- Selecting only the most relevant features enhances model accuracy and efficiency, improving the prediction performance of the predictors
- Minimized Overfitting
- Irrelevant features may cause overfitting, where the model excels on training data but fails on test data. Feature selection can prevent this.
- Greater Interpretability
- Models with fewer features are way easier to understand and explain to stakeholders, providing a better understanding of the underlying process that generated the data
- Accelerated Training and Prediction
- Reducing the feature set speeds up both the training and prediction proceses, providing faster and more cost-effective predictors
Feature Selection Techniques (Supervised)
1. Filter Methods
statistical method without modelling Target and individual feature 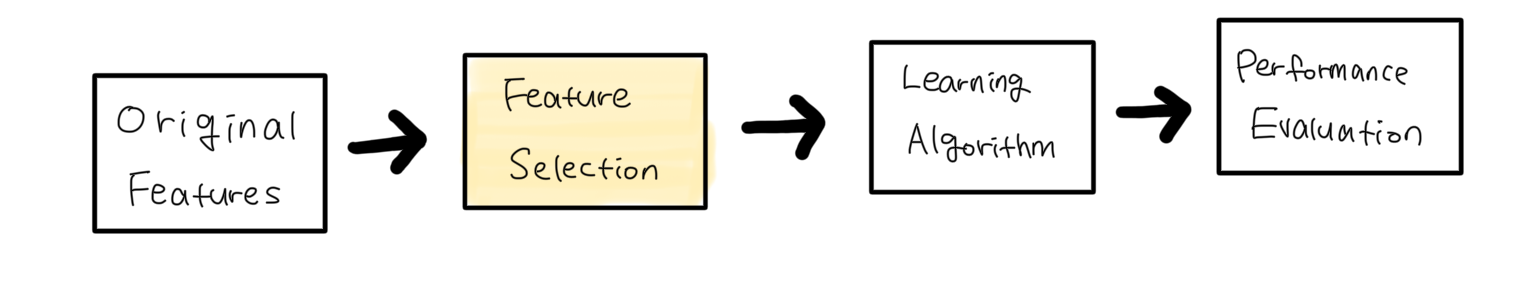
Filter methods evaluate feature relevance by applying statistical techniques to measure the relationship between each feature and the target variable individually. There are lots of techniques to try filter methods but common techniques here include the chi-square test(categorical), Information gain,Variance thresholding and Correlation coefficients.
This approach ranks feature individually based on their statistical properties rather than their interaction with a specific machine learning model, allowing for algorithm-independent feature selection.
This method is useful for evaluating the non-linear relationship between each feature and the target individually. Since each feature is assessed independently, it may miss complex interactions between multiple features. In particular, one-hot encoded features often provide meaningful information through interactions, but filter methods only assess each feature’s contribution to the target and model individually, without considering the overall model context.
Therefore, while filter methods are helpful as an initial step to remove irrelevant features, if you want to better capture interaction effects between features, model-based methods like Random Forest (RF) or Gradient Boosting (GBM) with feature importance are more beneficial. This is because model-based methods identify features that enhance predictive performance by including feature interactions within the overall model context.
본 방법은 각 피처와 타겟 간의 비선형관계를 개별적으로 평가하는 데 유용함. 각 피처를 개별적으로 평가하기때문에 여러 피처 간의 복잡한 상호작용을 놓칠 수 있음. 특히 원-핫 인코딩된 피처들은 상호작용을 통해 의미 있는 정보를 제공하는 경우가 많지만, 필터방법은 전체 모델 맥락에서 각 피처가 타겟과, 모델에 얼마나 기여하는지를 평가함. 그래서 처음에 타겟을 몇개 제거하는 예비단계로 유용하지만 피처 간의 상호작용 효과를 더 잘 반영하고 싶다면, RF나 GBM 같은 모델을 통한 Feature Importance 방법이 더 유용함. 왜냐하면 model based methods 는 전체 모델 맥락에서 피처 간 상호작용을 포함해 예측 성능을 높이는 피처들을 찾아낼 수 있기 때문.
(1) Variance Thresholding
Purpose
Variance thresholding removes features with low variance, under the assumption that features with little variation are unlikely to carry meaningful information.
Usage
Often used as a preliminary step, especially with high-dimensional data, to reduce the number of features wich has minimal impact on the model.
Limitations
Variance thresholding does not consider the relationship between features and the target variable. Features with low variance but strong predictive power may still be eliminated, so it’s best to use it as an initial filter.
(2) Correlation Coefficient
Types
- Pearson’s correlation
Measures linear relationships between continuous variables. - Spearman’s rank correlation
A non-parametric measure for ranked or ordinal data, which works well for monotonic relationships. - Kendall’s Tau
Often used with smaller samples or ordinal data.
Purpose
measures linear relationships between continuous variables, with values ranging from -1 to +1.
Usage
Target Correlation
High correlations with the target variable indicate potential importance.Inter-feature Correlation
High correlated features might indicate redundancy, so we might keep one and drop the others to avoid multicollinearity.
Limitations
Correlation measures linear relationship, so it may not capture non-linear dependencies. better to combine with other techniques to capture more complex patterns.
(3) Mutual Information
- Mutual Information & Information Gain
- Mutual Information is ideal for feature selection in a broad sense, evaluating each feature’s relevance to the target without model dependency. Information Gain is primarily used in decision tree algorithms to determine the best split points, focusing on class separation within the context of the tree.
Purpose
Mutual Information (MI) measures the amount of information shared between two variables, making it useful for identifying both linear and non-linear relationships between features and the target.
Usage
It calculates the reduction in uncertainty for one variable given knowledge of another. High MI -> more contribution to predict the target
Limitations
MI can be computationally intensive for large datasets, as it requires calculating the information gain for each feature individually. Additionally, MI does not account for inter-feature relationships, so it’s often used in conjunction with methods that do.
Summary of three filter methods
- Variance Thresholding
Quick initial filter, best for eliminating features with very low or no variance.
분산이 낮은 피처는 모델에 영향을 거의 주지않을 가능성이 크기때문에 초기 피처 필터링 방법으로 선호됨. - Correlation Coefficient
Identifies linear relationships; helps prioritize predictive features and remove redundant ones. 선형 관계만 측정 가능하며 피처와 타겟 간의 상관관계만 고려.
빠르고 간단하며 1차 필터로 유용하게 사용 가능하고 해석이 용이함.
타겟과 Correlation 높은 것은 남기되 변수들끼리의 Correlation 이 높은 쌍 중 하나의 변수를 지움. (다중공선성 제거를 위해) - Mutual Informations
Captures non-linear relationships with the target; useful for detecting features that add unique information to the model.
두 변수 간의 상호 의존성을 측정하는 방법으로, 한 변수의 값을 알 때 다른 변수에 대한 불확실성을 얼마나 줄일 수 있는지를 나타냄.
비선형관계도 잘 잡아냄.
범주형 데이터, 연속형 데이터 모두 적용 가능.
특정 ML 모델에 의존하지않음.
피처들 간의 복잡한 상호작용 반영 X. 피처와 타겟과의 정보량을 기준으로 선택이 이루어짐.
두 변수의 엔트로피(불확실성)를 이용해 계산되며 Mutual Information 값이 높을수록 해당 피처가 타깃에 중요한 정보를 많이 제공한다고 해석할 수 있음.
2. Wrapper Methods
Find the optimal combination Model-Dependent Evaluation not in the training phase but outside of model Iteratively
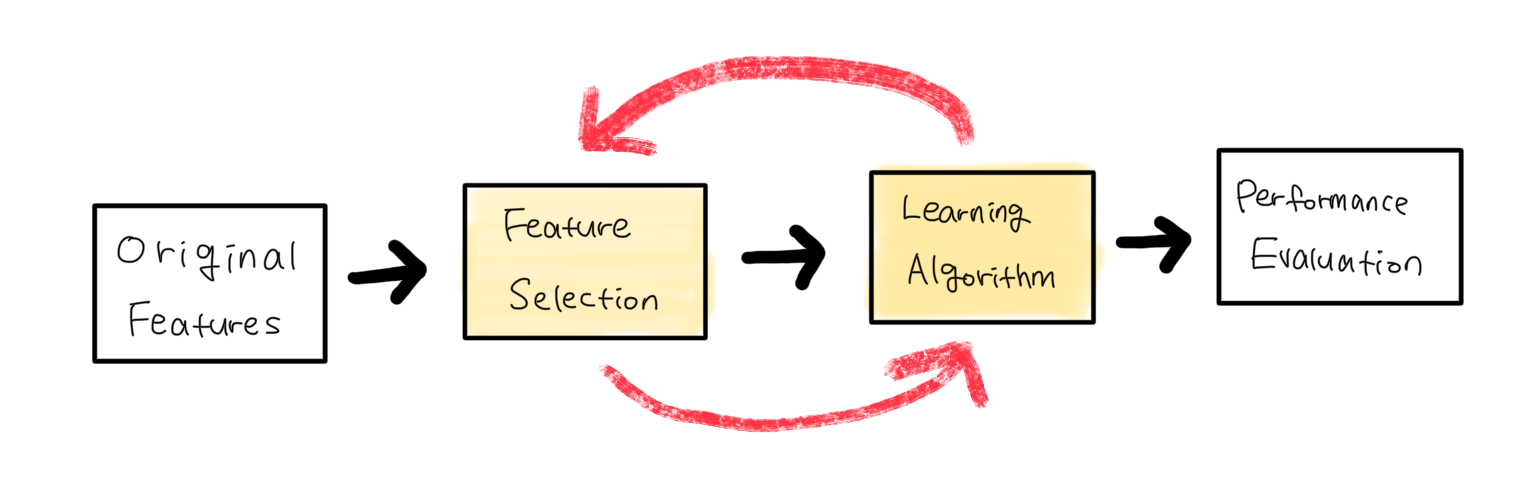
Wrapper methods search for the optimal combination of features by training models with various feature subsets using a specific ml algorithm to evaluate feature importance. They wrap the feature selection process around the model training and evaluate the model’s performance to determine the optimal subset of features.
Wrapper method follows a greedy search approach by evaluating all the possible combinations of features against the evaluation criterion.
여러개의 피처를 모델학습 시에 사용하여 가장 스코어가 높은 조합을 찾는다. (모델 학습을 피처의 조합 수 만큼 수행)
Limitations
They generally follow an iterative process where features are added or removed in a step-by-step manner, using model performance as a guide. So they are more computationally intensive than filter methods because they involve training multiple models. This can be costly, especially with large datasets or complex models.
Examples
- Forward Selection
- Backward Elimination
3. RFE (Recursive Feature Elimination)
A popular wrapper method where a model is trained, and features are ranked based on their importance scores. The least important features are removed, and the model is retrained. This process is repeated until the optimal feature set is reached.
- often used with models that provide feature importance scores, like decision trees or support vector machines.
- Efficient for identifying the most predictive subset of features, especially when combined with cross-validation to avoid overfitting.
3. Embedded Methods
Model-integrated Selection features selected during training phase Efficiency
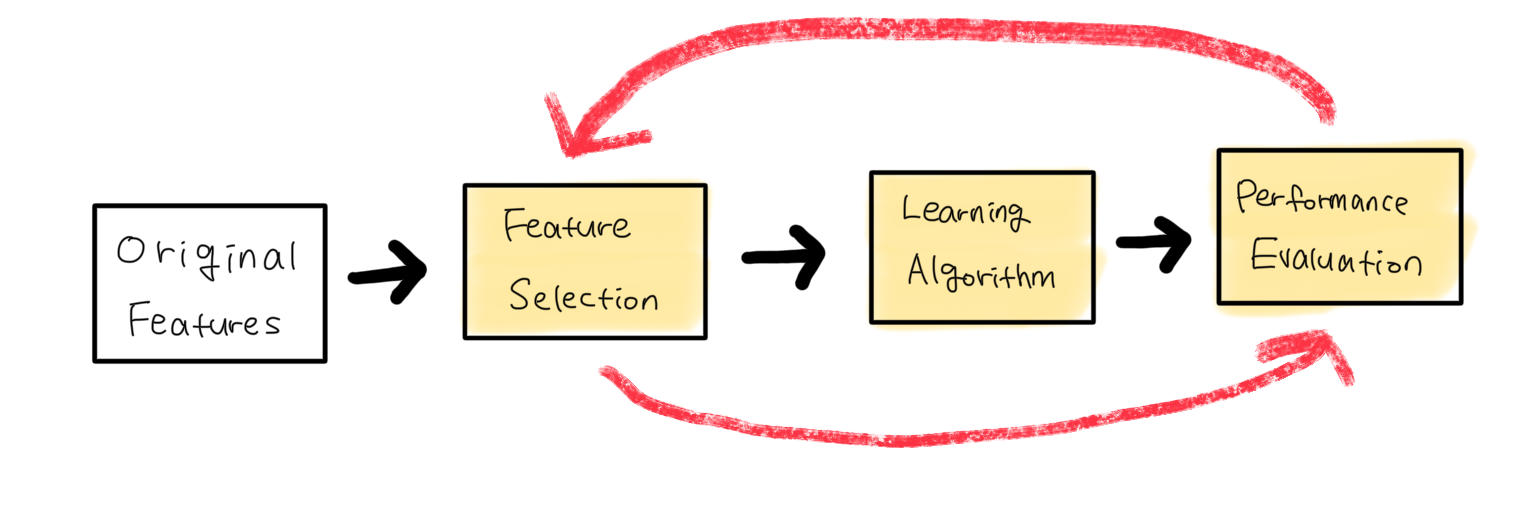
Embedded methods are techniques where the feature selection process is integrated directly within the training of a model. Unlike filter methods (which are model-independent) and wrapper methods (which evaluate multiple models on different feature subsets), embedded methods select features based on the contribution of each feature to the model’s performance as the model is being trained.
Feature selection is built into the model training itself, like penalizing less important features with L1 Regularization.
Model decides important features depending on how large coefficient and feature importance.
(모델 학습 1번 진행)
Examples
1. Lasso (Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator)
Lasso is a shrinkage method that performs both variable selection and regularization at the same time.
Lasso applies an L1 penalty, which forces some coefficients to zero. If a coefficient is zero then the feature is not taken into consideration, thus, it is in a way discarded.
Elastic Net is the combination of LASSO and Ridge Regression. This means, that it can also perform feature selection. Ridge Regression cannot do that since it only allows coefficients to be very close to zero but never actually zero.
- It is suitable when you have a large number of features and want a sparse, interpretable model.
2. Tree-based methods
such as RandomForests, ExtraTree, XGBoost which assign feature importance scores.
Wrapper methods consider unimportant features iteratively based on the evaluation metric, while Embedded methods perform feature selection and training of the algorithm in parallel. In other words, the feature selection process is an integral part of the classification/regressor model. Wrapper and Filter Methods are discrete processes, in the sense that features are either kept or discarded. However, this may often result in high variance. On the other end, the Embedded Methods are more continuous and thus, don’t suffer that much from high variability.
4. Hybrid Methods
They leverage the stregths of multiple techniques.
(Examples) Dimensionality reduction techniques, such as Pricipal Component Analysis(PCA) transform the original features into a lower-dimensional space while preserving important information.
Feature Engineering
involves creating new features or transofrming existing features to improve the model’s predictive performance. It focuses on extracting meaninful information from raw data and creating features that capture important patterns or relationships.
- Techniques
- Scaling and normalization of numerical features
- Encoding categorical variables(one-hot encoding, label encoding)
- Creating interaction terms(multiplying or combining features)
- Deriving new featrues from existing ones.
https://machinelearningmastery.com/an-introduction-to-feature-selection/
https://medium.com/@nirajan_DataAnalyst/understanding-feature-selection-techniques-in-machine-learning-02e2642ef63e
https://www.blog.trainindata.com/feature-selection-with-embedded-methods/
https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/feature-selection-embedded-methods-a7940036973f
