Anomaly Detection for Welding Defect Identification
Anomaly Detection
Feature Engineering
Sensor Data Analysis
Design
Built an end-to-end anomaly detection system to identify welding defects during battery manufacturing. Emphasis was placed on optimizing feature extraction from time-series sensor data and using both traditional and deep learning models for robust detection.
The goal was not to maximize traditional accuracy metrics but to detect as close to 99% of actual defects as possible in a real-time production setting.
Data
- Source: Time-series sensor data collected from laser welding equipment in production lines.
- Preprocessing: Applied Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) to convert raw signals into time-frequency representations for image-based classification.
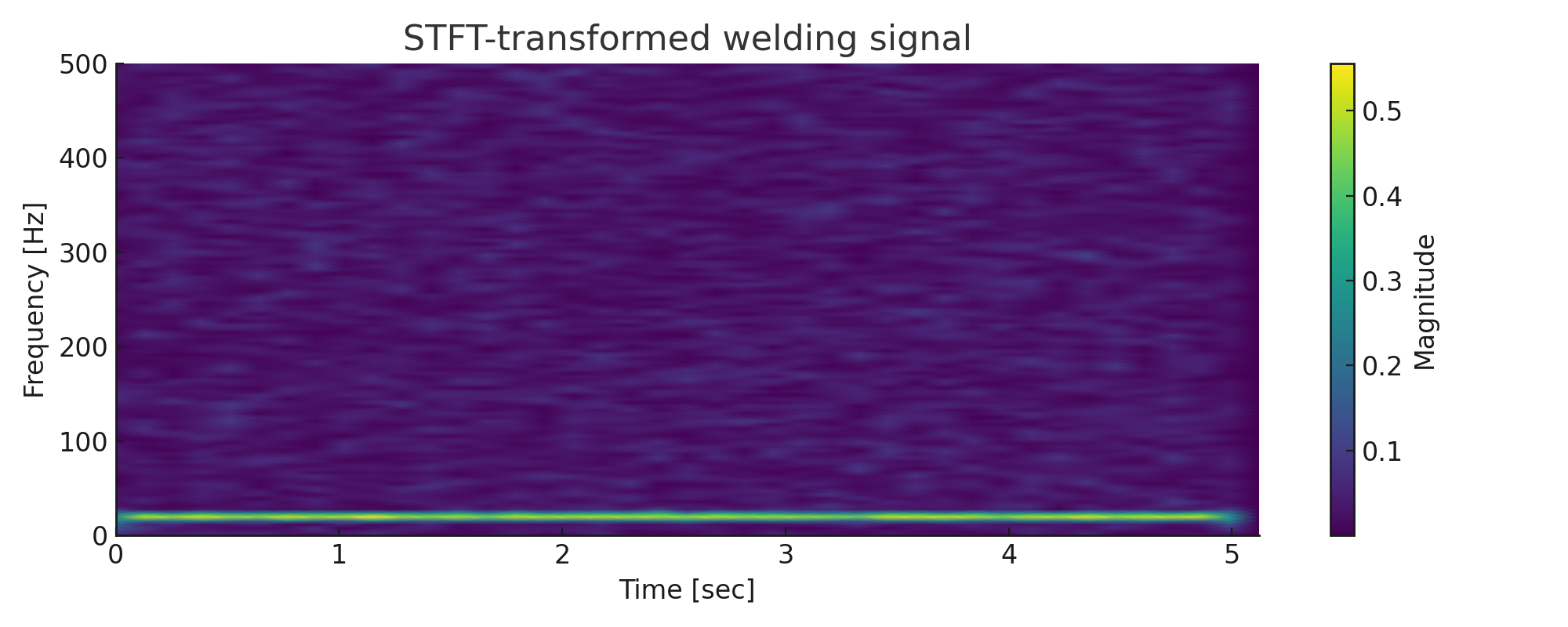
The image shows an example of a time-series sensor signal (top) and its corresponding STFT (Short-Time Fourier Transform) representation (bottom). The STFT transforms the raw signal into a time-frequency domain image, enabling the model to capture frequency patterns over time. This was particularly useful for identifying subtle anomalies in the welding process.
Main Models / Techniques
- Isolation Forest
- Local Outlier Factor (LOF)
- Support Vector Machine (SVM)
- 1D-CNN using STFT image input
- STFT / FFT
These models were compared in terms of their ability to detect anomalous patterns in sensor behavior, with CNN delivering robust performance when trained on STFT-transformed inputs.
Consideration
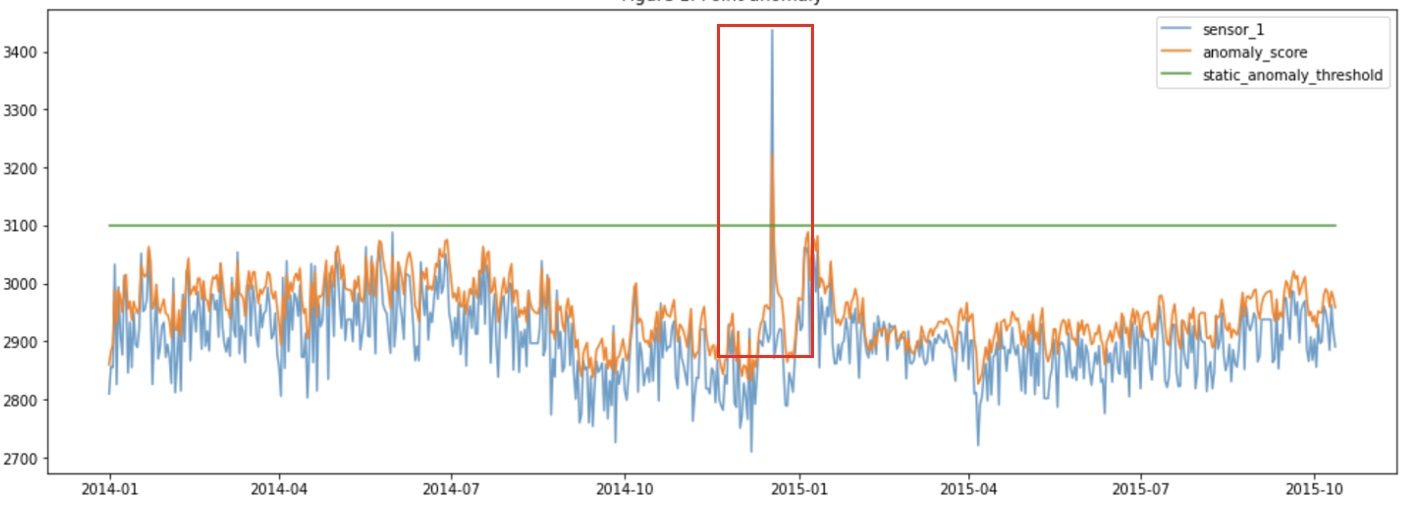
One of the most critical and challenging aspects of this project was threshold tuning. Determining the optimal cutoff for anomaly scores is essential for balancing false positives and false negatives in production environments. Fixed thresholds often led to either high false alarms or missed defects.
This required deep collaboration with field engineers who operated and maintained the welding equipment. Their domain knowledge helped define operationally viable and interpretable thresholds, integrating human expertise into model decisions.
Result
- Successfully implemented a real-time defect detection monitoring system in the production environment.
- The system was able to detect up to 99% of defective cases, greatly improving quality assurance compared to the previous manual method.
- Model predictions were integrated into a dashboard UI for live monitoring by on-site teams.
- Due to the lack of labeled data, traditional accuracy, precision, or recall metrics were not the main focus; instead, the primary success metric was the proportion of actual welding defects that could be flagged and intercepted early.
Future Ideas
- Automate and personalize thresholding methods using adaptive techniques.
- Explore ensemble detection frameworks that blend unsupervised and supervised signals.
- Collect more labeled data over time to enable more structured evaluation and model comparison.
